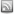Easily Duplicate a VGA Signal to Anywhere in the World
December 16, 2008 by Victor · Leave a Comment
Gone are the days of WebEx and high-priced license-based collaboration solutions. Epiphan Systems has introduced a simple yet powerful VGA-based conferencing product for online collaboration and monitor synchronization.
The VGA Bridge, promises to “bridge” the distance gap between two monitors or projectors, whether they be in the rooms next to each-other or accross the world.
It works by digitizing the analog VGA signal into a compressed digital format that is suitable for web broadcast and then sending it to the receiving VGA Bridge for uncomression and reproduction. While this is not a new concept in the world of web-enabled streaming content, the fact that the VGA Bridge can handle resolutions up to 1600 x 1200 in 100% lossless quality is a first. Of course, you would need a fast and stable Internet or Gigabit LAN connection in order to achieve transfer rates of up to 60 frames per second, but that is to be expected from such as high-end and specialized product.
If web-based collaboration, telemedicine, or remote monitor synchronization are critical to your application, we suggest that you seriously consider the VGA Bridge from Epiphan Systems.
Mini DVI, what it is and how to capture it
Mini DVI is a common connector found on Apple’s Macbook, Macbook Pro and Intel-based Powerbook G4 laptops that have been produced prior October 2008. A Mini DVI port can also be found on Apple’s Intel-based 1U XServe servers.
According to Apple, the creator and sole manufacturer of computers with Mini DVI ports, Mini DVI, like Mini VGA, was implemented to save space and allow for the production of smaller laptops. This, however has been disproven by other manufacturers like Dell or Toshiba which have all made notebook computers with similar sizes, form factors, and specifications to Apple’s, yet have been able to implement a full-size DVI port. The relatively steep price of the adapters manufactured by Apple to work with the Mini DVI port (over $50 for some models) hint at the real (financial) motives behind Apple’s decision to equip its computers with Mini DVI ports.
While the way that the port is named suggests that Mini DVI is just a miniature version of the full-size DVI port, the Mini DVI port actually carries three different signals:
- Single-link DVI (Digital)
- VGA (Analog)
- TV (Analog)
In order to convert the Mini DVI signal to any of the three signals mentioned above, a special adapter is required for each application.
1. Mini DVI to DVI (Single Link)
2. Mini DVI to VGA
3. Mini DVI to Video (TV RCA + S-Video)
A Mini DVI to HDMI adapter is also available on the market, but, unlike the three adapters shown above, is not manufactured by Apple.
Capturing Video from the Mini DVI Port
Since the Mini DVI port can be easily converted to DVI, VGA, or TV-out using adapters manufactured by Apple, a Mini DVI signal can be captured using a DVI or VGA frame grabber or a video capture card for TV/S-Video signals. Note that, since the DVI signal is single link, Mini DVI does not support resolutions higher than 1920×1200 @ 60Hz.
Please refer to our Frame Grabber Comparison Table to evaluate possible alternatives for VGA and DVI frame grabbers.
Technical Information and Specifications
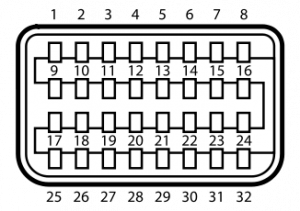
For advanced users doing custom product development based on Mini DVI, below is a pinout of the Mini DVI port. Source.
| Pin 1 | Dat2_P | Data 2 + |
| Pin 2 | Dat2_N | Data 2 - |
| Pin 3 | Dat1_P | Data 1 + |
| Pin 4 | Dat1_N | Data 1 - |
| Pin 5 | Dat0_P | Data 0 + |
| Pin 6 | Dat0_N | Data 0 - |
| Pin 7 | CLK_P | Clock + |
| Pin 8 | CLK_N | Clock - |
| Pin 9 | DGND | |
| Pin 10 | DGND | |
| Pin 11 | DGND | |
| Pin 12 | DGND | |
| Pin 13 | DGND | |
| Pin 14 | DGND | |
| Pin 15 | DGND | |
| Pin 16 | DGND | |
| Pin 17 | +5 V | |
| Pin 18 | DCC_DAT | |
| Pin 19 | spare | |
| Pin 20 | BLUE | Analogue blue |
| Pin 21 | not installed | |
| Pin 22 | GREEN | Analogue green |
| Pin 23 | not installed | |
| Pin 24 | RED | Analogue red |
| Pin 25 | Detect | |
| Pin 26 | DCC_CLK | |
| Pin 27 | spare | |
| Pin 28 | DGND | |
| Pin 29 | HSYNC | Horizontal sync |
| Pin 30 | DGND | |
| Pin 31 | VSYNC | Vertical sync |
| Pin 32 | DGND |
Your Complete Guide to VGA and VGA Capture
Whether your application involves creating IT instructional manuals, recording from high resolution security systems, sharing a presentation with people from around the world, or printing handouts directly from any computer screen, you are looking at VGA video capture or VGA signal capture as a mean to achieving these goals. This article will explain in-depth how VGA signal capture works and what you need to know in order to capture such a signal.
The VGA Plug
Unlike DVI or HDMI, which are both digital standards, a VGA signal is purely analog. The differences between VGA, DVI, and HDMI are described in detail in this article.
“VGA” is short for Video Graphics Array and has been the most common connector/plug for analog video on computer equipment and various electronics with an analog video output since the introduction of personal computers (PCs). VGA carries a RGB (red-green-blue) signal and is sometimes referred to as “D-Sub” due to its’ 15-pin “subminiature” connector. The term “VGA” also refers to the VGA standard graphics resolution – 640×480 pixels.
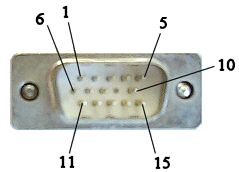
A detailed VGA pinout is shown below to help advanced users understand how VGA works. Source.
VGA Video Connector Pinout
| Pin # | Signal Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Red |
| 2 | Green |
| 3 | Blue |
| 4 | No Connect |
| 5 | Ground |
| 6 | Ground |
| 7 | Ground |
| 8 | Ground |
| 9 | No Connect |
| 10 | Ground |
| 11 | No Connect |
| 12 | DDC DAT |
| 13 | Horizontal Synchronization |
| 14 | Vertical Synchronization |
| 15 | DDC Clock |
VGA Frame Grabbers and How They Work
The only true way to capture and record a VGA signal is through a VGA-compatible frame grabber. A VGA frame grabber can be defined as a device that proccesses analog VGA signals and converts them into digital signals readable by computer equipment. While frame grabbers are described in slightly higher detain in this Wikipedia article, these three main internal components determine a VGA frame grabber’s performance:
- ADC (analog-to-digital) converter. This is the circuit that transforms the analog signal coming from the source VGA signal into a digital stream that can be read by the target computer.
- RAM (random-access memory). Also referred to as buffer memory, this memory is vital in storing the captured image for a short period of time on board the actual frame grabber.
- FPGA (field-programmable gate array). This is the heart of the frame grabber and is analogous to a processor inside a PC. It is a part that is entirely programmed by the manufacturer of the frame grabber.
Some frame grabbers, like the PixelSmart VGA Master have no on-board RAM buffer memory. This fact alone, besides leading to a lower-quality image, lowers the maximum possible capture rate (also referred to as frame rate) achievable by the frame grabber. Frame grabbers without on-board RAM are sufficient for the capture of presentations with lots of static slides or any other static imagery, like capturing screenshots from the computer’s BIOS. On the other hand, if you are capturing a high-resolution image and/or are capturing from a source with a high frame rate, like a video game console (ie XBOX 360) or medical equipment (ie: ultrasound), a frame grabber with at least 16MB RAM would be preferred. The VGA2USB Pro by Epiphan Systems, for example, has 32MB RAM memory and is able to capture at a whopping 60 frames per second in some resolutions.
PixelSmart’s Internal PCI VGA-Master
Epiphan Systems’ external USB-based VGA2USB Pro frame grabber
While RAM is important in defining the characteristics of a frame grabber and the quality of the image it outputs, another important factor is the way that the FPGA, or processor, is programmed. You will notice that the higher-end frame grabbers, like the VGA2USB Pro pictured above, have built-in features that some of the more basic frame grabbers, like the PixelSmart, do not have. A quick look at the Epiphan Systems webpage reveals the following features programmed via the FPGA processor: On-board cropping, Color space conversion, USB Transfer Accelerator™, Compression Booster Filters™. All of these software/firmware features allow the frame grabber to achieve extremely high quality and transfer rates without increasing the frame grabber’s size.
Please refer to our complete Frame Grabber Specifications Comparison Table for detailed and complete specifications on every VGA frame grabber on the market.
Applications for Frame Grabbers
Frame Grabbers, while being a niche product, have many practical uses in today’s IT-oriented business environment. The five most common and prominent uses are described in detail in our Top 5 Uses for High Resolution Frame Grabbers You Should Know About article. From the gaming industry to the military, frame grabbers are used accross many fields related to computer technology. To give you a general idea, some industry-specific uses for high resolution VGA frame grabbers are described below.
Computer Console Gaming
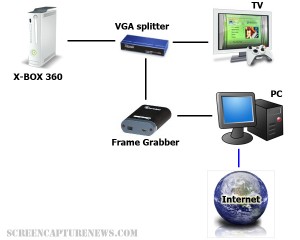
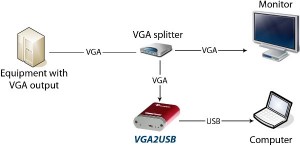
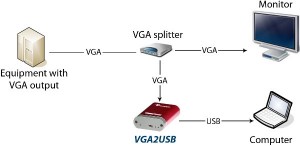
Microsoft’s X-BOX 360 gaming console has the ability to output its images via VGA or DVI. This means that a VGA frame grabber can be used to capture and record the gameplay from this game console, and even broadcast the gameplay live over the internet for other viewers to see.
The diagram above explains how to connect an X-BOX 360 to a frame grabber for recording and broadcasting the gameplay. The X-BOX’s VGA cable is connected to a VGA splitter’s input, from which one VGA output goes to the TV, and the other to the frame grabber-equipped computer. The image can then be broadcasted to the internet using the computer.
Presentation, Conference Broadcasting and Recording
In today’s globalized business world, businesses often have partners in many different countries. When conducting an online meeting or presentation, the presenter often has the need to share his screen with viewers around the world. For this exact reason, VGA frame grabbers are useful. They allow the presenter to not only share an image from a projector, but also from a BIOS screen, an ATM machine, a RADAR device, a medical ultrasound device, a security system, or even an electronic microscope. Most of these VGA sources are not able to be broadcasted in real-time with the use of traditional software sources, and frame grabbers are the only way to properly create diagnostic-quality images and videos from these devices.
In the diagram above, the VGA source is connected directly to a frame grabber-equipped PC with access to the internet. Using any web broadcasting software, the user is able to relay the images and video captured by the frame grabber to his or her audience.
Security System Surveillance Recording and Broadcasting
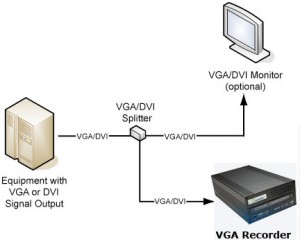
Today’s security systems and cameras are able to support digital formats as well as high resolutions required for complex security solutions. Of course, as solution is needed to record the outputs from the security system, store it in a digital format, and provide access to the files from remote locations. All of this can be accomplished with VGA frame grabber-based technology, such as the VGA Recorder, which have ample space for recording video files (up to 500GB), are able to directly transmit recordings to a remote FTP location, and give access to the recorded files through a web interface.
The diagram above, borrowed from the Epiphan Systems website, shows how easy it is to hook up a security system’s VGA output to the VGA Recorder. Everything can be set up in minutes, and the VGA Recorder is able to archive hundreds of hours of digital compressed video data to its internal hard drive.
Telemedicine and Remote Guidance
Telemedicine, also known as Remote Guidance, is an expanding field in which doctors are able to, through the internet, diagnose patients and provide advice. Telemedicine has many practical applications but some of the more notable ones are the delivery of expertise to areas in which it is not practical to have a qualified doctor at all times. For example, lets suppose that a player on a sports team gets a knee injury. Through telemedicine, the coach can use a portable ultrasound device like the Logiq Book XP and, with the aid of a frame grabber, relay the images from the Logiq Book directly to a qualified radiologist who can then make a decision on the severety of the injury.
The diagram above shows how any equipment with a VGA output, such as the ultrasound device, can be connected to a frame grabber, and the a computer. The images are then relayed to the qualified radiologist or doctor through the internet or a satellite uplink. If you would like to find out more about the field of remote guidance, then this website is a good start.
Summary
The VGA signal is the most common format used on today’s electronics and computer-based equipment. When this equipment is coupled with a VGA frame grabber, the possibilities are endless. Using a frame grabber, which is a relatively inexpensive device, organizations can not only significantly cut costs, but can also improve their productivity.
Top 5 Uses for High Resolution Frame Grabbers You Should Know About
September 12, 2008 by Victor · Leave a Comment
High resolution frame grabbers are devices that are used to capture the signal from a VGA or DVI stream and convert it into a readable computer format. In other words, frame grabbers take a high resolution video signal and relay it to the memory of the computer as digital data. What you do with that data, however, is entirely up to you. This article will list the top most useful applications for modern high resolution frame grabbers.
1. Archiving Images and Video
This is probably the most common use for frame grabbers today. All high resolution frame grabbers come packaged with an application that allows you to capture the VGA/DVI signal to old fashioned MPEG or AVI video as well as common JPG, BMP, or GIF images. Some applications even have support for live resizing of the captured output in order to decrease file size.
As well, if the frame grabber has WDM driver or Video4Linux support, the computer sees it as a high resolution camera, meaning that you can use any application, such as Windows Encoder, QuickTime Broadcaster, or Adobe Premiere to capture from your VGA or DVI source. Furthermore, SDKs and APIs released by manufacturers allow one to create custom applications and integrate the frame grabber into existing solutions, therefore automating the archiving proccess.
This diagram, taken from the Epiphan Systems website, shows how to use a frame grabber for recording images or video from any device with a VGA output while keeping the device’s monitor. The monitor can be omitted if the user does not need to view the output from the device.
2. Broadcasting
Broadcasting isn’t exactly the first thing that comes to mind when you are thinking of frame grabbers. It is, however, one of the top uses for high resolution frame grabbers. You may not know it, but pretty much all manufacturers that sell boxes for broadcasting a high resolution video signals have integrated frame grabbers inside their devices.
In fact, you can build an equivalent to one of these video/VGA/DVI broadcasting boxes yourself at a fraction of the cost by combining any high resolution frame grabber with a PC. As an example, this process is described in the “Broadcasting” section of our Epiphan Systems VGA2USB LR review.
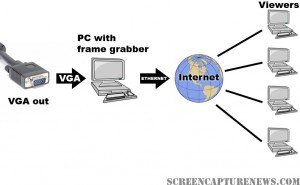
The simple diagram above explains how the broadcasting process works with a frame grabber. The VGA signal is digitized in real-time using the PC with PCI or USB frame grabber. Then, using webcast programs such as Wirecast, Windows Encoder 9, or QuickTime broadcaster, the digitized real-time video from the frame grabber is relayed over the internet to viewers worldwide.
3. Printing
This is an example of combining a technology that has been around for as long as computers existed (digital printing) with a fairly recent technology (frame grabbers). Why would you want to print to paper from the VGA or DVI output of a device? Often, a “hard copy” provides to be the most secure way of storing something.
Consider a situation where you are giving a presentation and would like to produce handouts for everyone on the spot. Wouldn’t it be great if you could just press a button and the contents of your screen got printed right away? Some manufacturers provide this feature in their software, while others (primarily Epiphan Systems) go as far as separate stand-alone devices dedicated to printing from a VGA screen.
The diagram above, taken from the Epiphan Systems website, shows how a frame grabber based VGA printer is connected to the source device. The VGA printer, shown in a black enclosure, can be replaced with a PC and frame grabber combination.
4. Web Conferencing
Distance collaboration forms the basis of many partnerships in today’s complex business environment. Several characteristics define a good web conferencing solution – reliability, ease of use, effectiveness.
Pairing a frame grabber with your conferencing software of choice can give you these three characteristics and more. Solutions like WebEx allow the user to share his or her webcam. Since most frame grabbers register as a high-resolution camera in Windows and Mac OS X, the user can simply point the program to transmit images from the frame grabber instead of from a webcam. This can be extremely useful when you want to share images from an external source other than the computer being used for the web conference. This can include anything from X-Ray imagery, live ultrasound scans or live GPS info to relaying live screenshots from a server or computer.
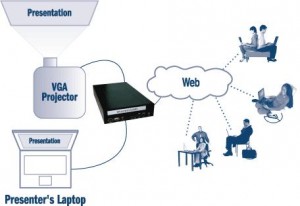
Epiphan Systems makes the VGA2WEB, which is a one-of-a-kind web conferecing solution with the primary goal of sharing a VGA signal. If VGA signal broadcasting and conferencing is critical to your application, then this may be a product you should seriously consider.
This diagram, taken from Epiphan Systems, shows how a presentation is broadcast in real-time to viewers on the web. The setup for web conferencing is identical to the setup for broadcasting. In the case of conferencing however, the user has a medium in which he/she can give feedback to the presenter.
5. Monitoring of Critical Systems
Most of today’s IT equipment has VGA or DVI outputs, many of which need to be monitored as they are critical to the functions of the organization which they support. Traditional methods of using VNC, converting the VGA to composite video, or having a separate monitor for each output have proven to be not only costly, but also not very reliable.
Unlike substitute solutions, high resolution frame grabbers are very scalable, meaning that many of them can be installed on one computer with one monitor output that will be used for central monitoring. Frame grabbers can also be mounted into a rackmount system and you will find that some manufacturers are ready to custom-build a rackmount frame grabber for you.
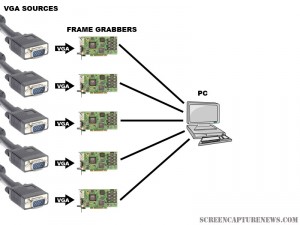
In the diagram above, several frame grabbers, each of which are connected to separate VGA sources, are attached to one computer. This computer displays the output from each VGA source on one monitor. As well, the computer can record, broadcast, or print from each of the sources in real time.
Emulate a screen capture card on your computer… for free!
September 2, 2008 by Victor · Leave a Comment
Have you ever wanted to use your video capture software of choice for creating screen captures, broadcasting live from your screen, or creating videos? Are you a software developer that would like to integrate screen capture into your software package? If your answer to one of these questions is “yes” then we have a solution for you… for free!
The solution is to use a free tiny (<1MB) utility called VH Screen Capture Driver by Hmelyoff Labs. VH Screen Capture driver works by emulating a video capture card in your Windows system, with the output being that of your local monitor. Think of it as a software-based frame grabber that works on Windows machines only. However, do not think of this software as complete replacement to frame grabbers, as it has many major disadvantages over its’ hardware counterparts.
First of all, the screen capture driver uses up a vast amount of system resources, meaning that more advanced applications will not have good capture quality, whereas a frame grabber uses its’ own resources only and puts no extra load on the system. The VH Screen Capture Driver is also only compatible with Windows machines and, being a DirectShow filter, will not work with all applications. A frame grabber however, is compatible with any VGA or DVI output, whether it be from a MAC, Windows machine, high-resolution navigational equipment, etc. Thus, VH Screen Capture is good as a free solution but in no way can this software match all of the advantages that frame grabbers entail.
Technically, however, VH Screen Capture Driver is a DirectShow filter and is compatible with applications that use DirectShow to display content on the user’s screen. The output frame rate does depend on which application is being captured and the system load.
In short, VH Screen Capture Driver allows the user to use popular video capture and broadcast applications, such as Windows Media Encoder and Adobe Premiere, without native screen capture support to grab the image off of their screen.
Using VH Screen Capture Driver
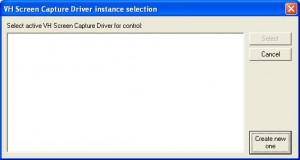
Step 1: Install the program and run it. You should immediately see the following screen. Press “create new one” to start a new instance of the capture driver.
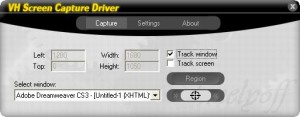
Step 2: You will now see a configuration window. Under the “Capture” tab, you may choose the “Region” option and select only a region of the screen to broadcast. Ticking the “Track window” option enables you to broadcast a single application. You may select it by choosing it from the drop-down list or by clicking on the crosshairs beside the drop-down list and then selecting the application.
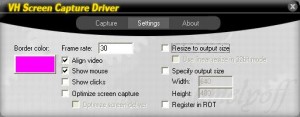
Step 3: Now select the “Settings” tab. Here you can adjust the maximum output frame rate, whether to show your cursor, or whether to compress the screen capture output. If you would like to resize your output in real time, the “Resize to output size” option must be ticked and the output size (Width/Height boxes) must be specified. This is most useful when you are broadcasting to the web and would like to limit the output video resolution in order to use less bandwidth or obtain a smaller file size.
Congratulations! The VH Screen Capture Driver is now configured. Now go to your video capture application of choice, select the “VH Screen Capture Driver” as an input, and start capturing!